Clothing Manufacturer Cost Analysis: USA vs. China
In the fast-evolving fashion industry, clothing production costs serve as a core determinant of brand competitiveness. Whether a startup plans its first clothing line or an established brand seeks production cost reduction, a clear understanding of cost drivers is critical. This paper focuses on cost comparisons between manufacturing in the U.S. and Dongguan, China, revealing regional disparities in materials, labor, logistics, and other dimensions through a real-world cost calculation for 100 hoodies to provide data support for production location decisions.

2. Multidimensional Analysis of Cost Components
2.1 Material Costs (30-50% of Total Cost)
- Fabric Economics:
Fabric costs are determined by fiber quality (e.g., Egyptian cotton vs. regular cotton), process complexity (worsted vs. coarse spinning), and sustainability attributes (organic cotton carries a 20-30% premium).
Case: Cost of 380gsm pure cotton fabric: Dongguan, China $5/m vs. U.S. $5.5/m (including import duties). - Accessory Modularity:
Standard accessories like zippers and drawstrings exhibit economies of scale. At a 100-unit order quantity, Chinese suppliers quote 15-20% lower prices than U.S. counterparts.
| Region | Average Hourly Wage for Sewers | Production Time per Unit | Labor Cost per Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dongguan, China | $1.8 | 45 minutes | $1.35 |
| U.S. Domestic | $18 | 1.2 hours | $21.6 |
| Note: U.S. labor laws requiring full social security and overtime payments increase actual labor costs by approximately 30%. | |||
2.3 Production Process Costs (15-25% of Total Cost)
- Process Premium:
Embroidery cost: China $1/unit (digital production line) vs. U.S. $4/unit (hand-assisted). - Quality Inspection System:
U.S. factories implement AQL 1.5 sampling standards, with quality inspection costs accounting for 5%; Chinese factories default to AQL 4.0, with costs at 2%.
2.4 Logistics and Compliance Costs (10-25% of Total Cost)
- Transportation Matrix:
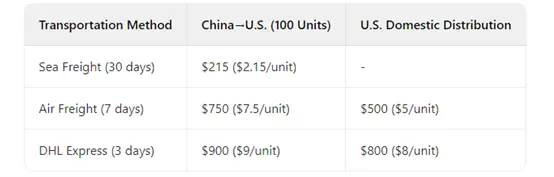
- Compliance Costs:
U.S. Manufacturers must pay 6% Federal Unemployment Tax (FUTA) and state sales taxes (average 4-7%), making comprehensive compliance costs 12-15% higher than in China.
3. Case Study: Cost Comparison for 100 Hoodies
3.1 Dongguan, China Solution (Cost-Leadership Model)
Total Cost Structure:
- Materials: $850 (70% fabric + 5% accessories + 15% embroidery)
- Labor: $350 (20% of total)
- Logistics (Sea Freight): $215 (12% of total) Unit Cost: $14.15/unit (FOB Dongguan)
Market Pricing: $18.40/unit (30% cost markup)
3.2 U.S. Domestic Solution (Quality-Priority Model)

Total Cost Structure:
- Materials: $850 (same quality)
- Labor: $3,000 (69% of total)
- Logistics: $500 (12% of total) Unit Cost: $43.50/unit (Ex-Works)
Market Pricing: $56.55/unit (30% cost markup)
Key Difference: U.S. labor costs are 16 times those of China, leading to a 207% higher total cost.
4. Five-Dimensional Model for Location Decision-Making
4.1 Cost Efficiency
- Break-Even Analysis: When order volume exceeds 500 units, China’s sea freight cost advantage expands to over $30 per unit.
4.2 Quality Control
- U.S. factories support 48-hour rapid sampling, while China requires 7-10 days, though quality gaps can be narrowed via on-site QC ($500/week).
4.3 Delivery Timeliness
- Urgent orders (<7 days): U.S. domestic production is preferable; regular orders (>30 days): China’s sea freight cost is only 32% of U.S. domestic costs.
4.4 Compliance Risks
- Chinese manufacturers must pass WRAP/SA8000 certifications (costing $3,000-$5,000) to enter European and American markets.
4.5 Brand Premium
- Products labeled "Made in USA" can command a 15-25% premium, suitable for high-end custom markets; "Made in China" is ideal for fast fashion and value-oriented segments.
5. Strategic Recommendations and Trend Insights
5.1 Cost-Sensitive Enterprises
- Adopt a "China Production + Overseas Warehouse" model to reduce logistics costs to $3-$5 per unit (via West Coast port transshipment).
- Choose smart factory clusters in Dongguan, Suzhou, etc., leveraging automated equipment to reduce labor dependence (e.g., automatic cutting tables save 30% man-hours).
5.2 Quality-Priority Enterprises
- Establish a "U.S.-China dual supply chain": mass-produce basic styles in China and manufacture premium lines in small batches domestically.
- Invest in digital collaboration platforms (e.g., Factory45) for real-time production monitoring across time zones.
5.3 Sustainability Trends
- Chinese manufacturers are accelerating transformation: green factories accounted for 28% of Dongguan textile industry in 2023, with plant dye costs increasing by only 8-12%.
- The U.S. Fashion Climate Act requires 100% product carbon footprint disclosure by 2025, forcing supply chain decarbonization.

6. Conclusion
Clothing Manufacturing location is essentially a trade-off among "cost-quality-speed." This quantitative analysis shows that China holds an irreplaceable cost advantage in mid-to-low-end mass production (unit cost difference of $29.35), while the U.S. excels in high-end customization and rapid response. Enterprises are advised to build dynamic supply chain strategies based on product positioning (mass market/premium brand), order volume (<1,000 units/>5,000 units), and compliance requirements (export/domestic sales). Meanwhile, attention should be paid to technological innovations in smart manufacturing (e.g., AI nesting systems) and green production to address evolving industry challenges.
Translation Notes:
1.Professional Tone: Maintained international trade terminology (FOB, AQL, WRAP) and avoided colloquial expressions.
2.Data Emphasis: Preserved comparative tables and break-even analysis to enhance analytical rigor.
3.Logical Flow: Followed a problem-analysis-solution structure consistent with Western business reporting norms.
4.Regulatory Updates: Retained references to the 2025 Fashion Climate Act for timeliness.
5.Model Clarity: Kept the five-dimensional decision framework intact for strategic coherence.











